Are you searching for How To Boost wifi Speed? This guide is for you, You will get tips and tricks to improve your wifi internet speed. All tips and tricks work out for sure.
Slow WiFi is one of the most annoying computing issues. Whether you’re working from home, binge-watching Netflix, or streaming your games on Twitch, slow internet speed is irritating. Even if you have gigabyte fiber connected to your router. It doesn’t matter if you have the best wiring outside your home; eradicating slow speeds and Wi-Fi dead zones is largely up to you.
I recommend you make some hardware changes you can do to eliminate dead spots and improve your home upload and download speeds. So, in this article, we’ll go over software fixes and modifications you can apply to your existing gear. If those changes don’t work, upgrading to a mesh network or purchasing a WiFi extender can help you enhance your wireless internet speed.
To get your WiFi speed back to normal, try following changes to your router and other devices.
Reasons Of Slow wifi Speed
Many things affect your network’s performance. If you live in a crowded household with multiple people utilizing wireless devices over WiFi, your internet speeds may decrease for a variety of reasons. Slow internet speeds are inconvenient if you work from home and require video conferencing, large data uploads, and downloads, or love streaming videos or gaming at the end of the day.
Let’s discuss the points firstly that slow down your wi-fi internet speed.
Physical Interference

WiFi interference may be slowing down your internet. The greater the distance the signal has to travel, or the more it has to pass through and around, the slower the speed. Physical obstructions such as walls or appliances, as well as the multitude of devices connected, all contribute to slower WiFi speeds.
Outdated WiFi Router

If your router is old, too slow, or simply not suited for modern connections, you may notice reduced upload and download rates. Certain older models of modems and routers are incapable of producing gigabit+ speeds.
Furthermore, if your modem is nearing the end of its life, it may have problems connecting to your service provider. It may be time to consider upgrading your technology to the latest and best products and services available.
Supporting Device
Some electronic devices cannot handle higher speeds. Check the owner’s manual or do an online search with the device’s model number to find out what speeds it can support.
Outdated firmware
It is also probable that your equipment is using older drivers or firmware. Drivers and firmware allow your gadgets to establish WiFi connections. The software contained in your equipment, such as your router and modem, maintains their security and optimal functioning. So, outdated firmware can cause your router or modem to slow down your internet connection.
Malware Or Virus

Firewalls, antivirus software, and virtual private networks (VPN) can interfere with your network. Firewalls or antivirus software on your computer or smartphone might slow down connection speeds because they constantly monitor data for malware or viruses before allowing it through. A VPN encrypts data to preserve your privacy, but it can also cause poor performance.
Test Internet Speed

It’s simple to believe that your internet connection is performing at its best. However, this is not always true. Testing your internet speeds can reveal whether or not there is a problem with how quickly data moves across the network, or if there are issues with specific devices. Testing will allow you to assess whether you’re getting the most out of your internet bundle or whether you need to upgrade your service to boost and better speed.
Steps To Boost wifi Speed
I am adding few points down below to increase or boost your wi-fi or internet speed that actually works.
1. Move Your Router

What about the router in the closet? Definitely not a good idea. Walls, closets, and even bookshelves can all degrade your Wi-Fi signal. Physically repositioning the router can significantly improve the speeds and range of its wireless transmissions. The ideal location depends depend on your home, but avoid placing your router in a corner, beneath a cupboard, or inside a drawer—the more central and visible it is, the better.
You may need to use some creative cabling to move your router to a better position, but the work will be worthwhile. The idea is to position your key devices (consoles, laptops, etc.) as close to your router as feasible. Devices that do not require a large amount of bandwidth, such as smart thermostats, do not need to be physically close.
As a result, while selecting a router, it is important to examine its appearance. If you buy a router that you think is awful, you are considerably more inclined to keep it in a closet. Determine the optimum placement for your high-priority gadgets, and then think about what will look well in that location. If you don’t have a level surface at the ideal location, you can place your router halfway up a wall. If possible, keep it away from other devices that emit electromagnetic waves, such as baby monitors, wireless keyboards, and microwaves.
2. Use an Ethernet Cable

The existence of cables is simple to take for granted. A wired connection to your router is faster and more reliable than Wi-Fi, and it is unaffected by other gadgets or huge fish tanks. The disadvantage is that it limits the location of your devices and makes them less convenient.
Still, for technology that requires the quickest possible internet connection—a gaming console, desktop PC, or streaming box, for example—running a wire is frequently well worth the effort. The router will have a few Ethernet connections available.
3. Change wifi Band

Wi-Fi signals are separated into channels. Your router communicates with your home’s gadgets via a specific Wi-Fi channel. If you have close neighbors with routers on the same Wi-Fi channel, everything can soon get congested. Changing channels can address this problem.
Each router will handle this differently. If you’re not sure, check its manual or search up the instructions online; however, the option should be available somewhere in the device’s settings. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are the best to attempt because they will cause the least interference when several devices are connected.
Most routers now use dual-band technology, which broadcasts at both 2.4 and 5 GHz frequencies. If your network settings allow it, you may be able to prioritize one over the other for specific devices—the 5-GHz band provides a speedier internet connection but has a shorter range than 2.4 GHz. We recommend leaving both frequencies enabled because older devices frequently only work at 2.4 GHz.
Also Read About: 2.4GHz vs 5GHz: Choosing the Right WiFi Band for Your Home
4. Upgrade Router / Modem

Upgrading your router or modem can significantly enhance your WiFi signal, providing a faster and more reliable internet connection. As technology evolves, newer models offer advanced features and improved performance, making it a worthwhile investment for users seeking better connectivity.
Modern routers and modems support the latest WiFi standards, such as 802.11ac or 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), which deliver higher data transfer rates and better handling of multiple devices. These devices often come equipped with advanced antennas and beamforming technology, allowing for more efficient signal transmission and extended coverage.
In addition to speed and coverage, security is another crucial aspect of newer router models. Upgrading ensures that you benefit from the latest security protocols and firmware updates, protecting your network from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
5. Use Mesh Network To Boost wifi Signal

Mesh network systems have emerged as a powerful solution to enhance and extend Wi-Fi signals in homes and businesses. Unlike traditional router setups, mesh networks consist of multiple interconnected nodes that communicate with each other, creating a seamless web of coverage. This innovative architecture effectively eliminates dead zones and ensures consistent connectivity throughout a space.
The nodes, or access points, in a mesh network work together to relay data, optimizing signal strength and distribution. This collaborative approach not only boosts Wi-Fi signals but also enhances network reliability. As a user moves within the network, the system intelligently directs traffic to the nearest and most efficient access point, maintaining a stable and high-speed connection.
One notable advantage of mesh networks is their scalability. Users can easily expand coverage by adding more nodes, and adapting the system to the specific layout and size of their environment. Additionally, mesh networks often come equipped with advanced features like self-healing capabilities, where the network automatically reconfigures itself to accommodate changes or disruptions.
6. Wi-Fi 6E

Wi-Fi 6 has only recently made its way into the majority of the devices and routers and Wi-Fi 7 is already in development. Then there’s WiFi 6E. What does it all imply, and what should you get? Wi-Fi 6E enables access to the new 6 GHz band which translates into 1200 MHz of clean spectrum in the US and much of the rest of the world and nearly 500 MHz of clean spectrum in the EU. This represents the single largest allocation of unlicensed spectrum in history and nearly triples the spectrum available for Wi-Fi. The “E” in Wi-Fi 6E stands for “Extended” since Wi-Fi 6E extends the capabilities of Wi-Fi 6 to the 6 GHz band for more capacity, wider channels, and less interference.
If you are able to purchase it, then go for it. Wi-Fi 7, the successor to Wi-Fi 6E, provides quicker connections for more devices, resulting in faster internet overall. Wi-Fi 7 will aid in the delivery of high-quality video and enhanced cloud gaming, as well as AR and VR applications that require fast throughput and low latency, both of which Wi-Fi 7 enhances.
7. Use Wi-Fi Extender
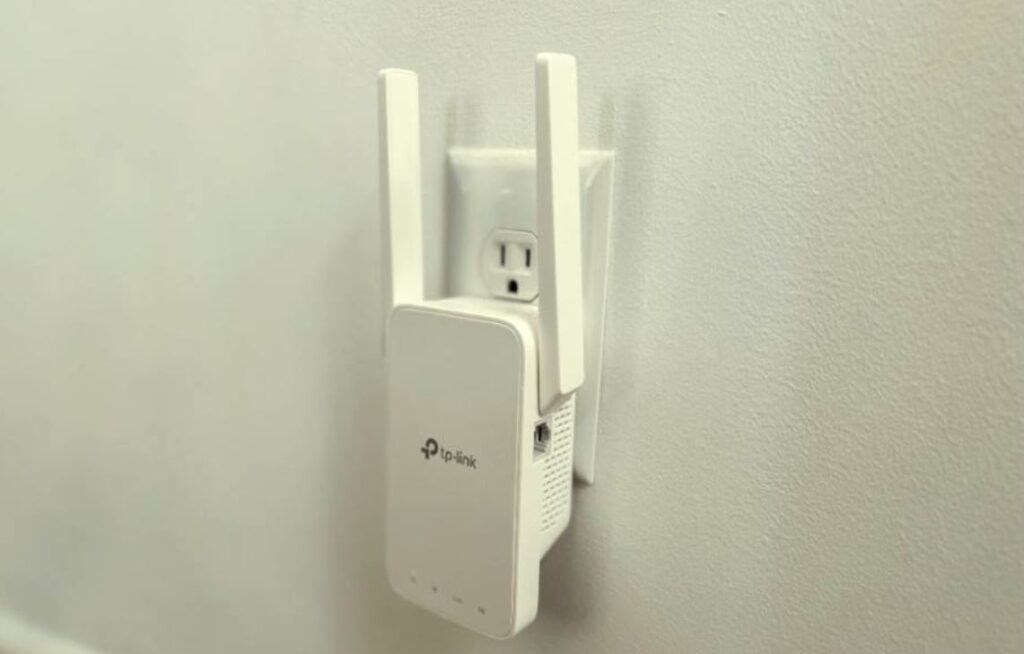

If engaging in with your router settings sounds too complicated, and you have a little cash to spare, consider purchasing a Wi-Fi extender or repeater. These devices plug into a spare wall socket, connect to the wireless internet transmitted by your router, and extend it.
They’re (usually) quick to set up, straightforward to use, and can instantly eliminate Wi-Fi dead zones in your home. The extended or repeated wireless signals will not be as strong compared to those originating directly from your router, thus location is key. Try using these devices to connect devices that do not require a lot of bandwidth.
8. Use Power Line kit
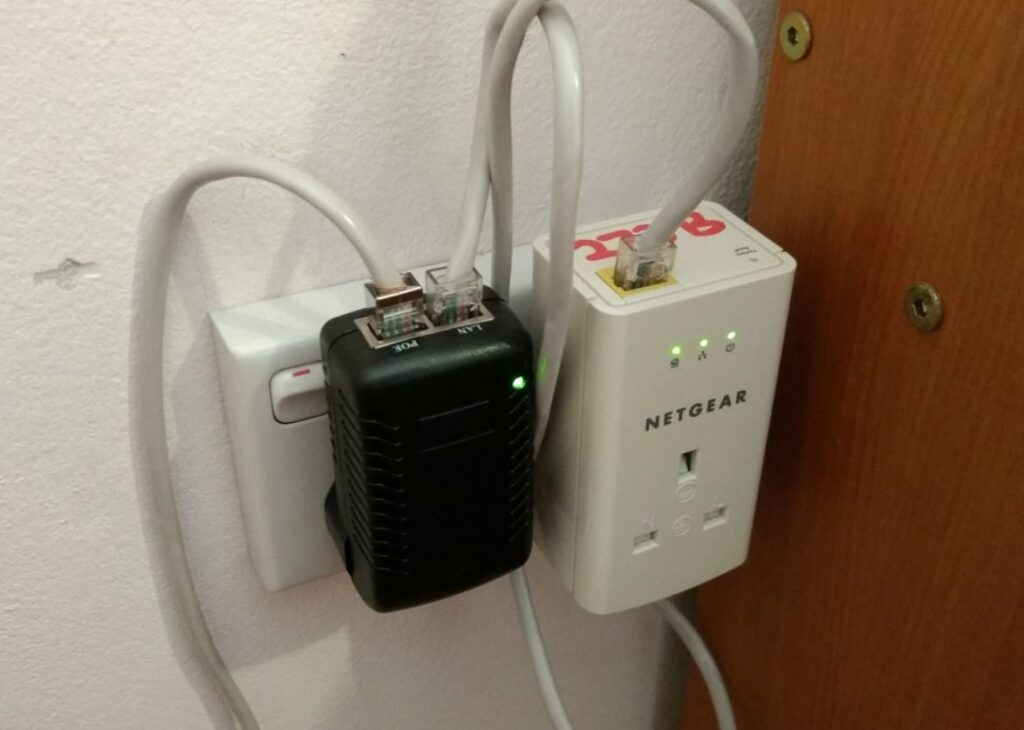

Power line kits are an alternative to extenders. Digital signals can pass via electrical wiring, and power line devices are intended to take advantage of this. Several vendors produce power line networking kits.
It works like this: you attach a power line plug to your router and then plug it into a wall outlet. Add another power line outlet in any other room of your home to provide a wired or wireless connection. There will be some reduction in speed, but it is a simple and effective solution. Unless your property is quite old, it should have electrical wiring that allows for this, but it’s advisable to purchase your kit from a merchant with a strong return policy just in case.
9. Password Protected

We probably don’t need to inform you, but your Wi-Fi network requires a password. In addition to protecting you from hackers, it prevents your neighbors from using your bandwidth for things like Netflix, which can reduce your speed. Make sure to utilize AES encryption, which is the most secure and fast security option.
10. Check For Connected Devices
Having a number of devices connect to Wi-Fi at the same time can be challenging. Plug anything you can into Ethernet and unplug anything you don’t need. Ensure that only the items that require internet have access to it.
Good routers include controls for prioritizing a certain device or service. It’s a convenient technique to ensure that your games are never interrupted by someone else streaming videos on Facebook.
11. Check Task Manager
This tip is specific for computers: If your PC or laptop’s internet is consistently slow but other devices appear to be working smoothly, launch Task Manager or Activity Monitor and check to see which programs are running in the background. Certain programs that do not need to be updated may be programmed to do so automatically. If they are constantly upgrading in the background, this could be the source of your slow connection. Check it out and change the parameters.
12. Restart Modem / Router

We had read this tip several times on the internet, but we were doubtful. Restarting your router on a frequent basis appears to be an extension of the age-old pseudo-solution for everything digital: reboot it. Yes, we know that restarting your router can sometimes prevent a dead internet connection, but we questioned router manufacturer Netgear if rebooting your router on a regular basis helps things speed up. The quick answer is: probably not.
Netgear’s vice president of product management, Sandeep Harpalani, said the company does not recommend rebooting routers “unless you actually encounter issues with connectivity or slowdowns due to radio frequency interference.” He adds that if you’re still utilizing 2.4-GHz Wi-Fi and experiencing performance issues, restarting may assist, as it forces the router to select the best channel with the least interference at boot-up. If you’ve upgraded to 5 GHz, it will automatically select the channel with the least amount of interference.
In either case, there is no necessity to reboot on a regular basis. If you are experiencing chronic troubles, restarting your router may be beneficial, but for the most part, stick with our other suggestions.
13. Call A Technician / Internet Service Provider

If you have tried everything and are still having problems, contact your internet service provider. They may dispatch a service expert, who may be able to identify an unnoticed issue preventing you from enjoying speedy Wi-Fi.
Final Wordings
Enhancing Wi-Fi speed involves a combination of strategic measures to optimize your network performance. Firstly, selecting the right placement for your router and minimizing interference can significantly impact signal strength. Additionally, upgrading to a modern Wi-Fi standard, such as Wi-Fi 6, and ensuring firmware is up to date can unlock faster data transfer rates. Implementing security measures to prevent unauthorized access and bandwidth hogging is equally crucial.
Thank you For Choosing Us.

